Unlike previous specifications of CSS, CSS3 has been split into modules as a way to control the complexity of any given piece of the large undertaking as well as provide user agents a clear means to carve out which areas they may not support due to technical device limitations. To clarify, the term "User Agent" is used for the broad category of anything that can consume a web document. User agents include the typical web browser but also tools such as screen reading applications, feed readers, Google and other search engine spiders, and other programmatic interfaces.
It will be imperative for you to make yourself familiar with rule sets in regards to CSS and the proper way to utilize inline styles and inline scripts. Lack of the aforementioned can and will render the examples useless because you will not be able to view the intended results through the "Try-it Editor".
The CSS3 specification opens itself up fort more formatting options. You will be able to specify multiple background images for an element, set the transparency of colors, allow certain elements to be resized on the fly, and add drop shadows to text and other elements dynamically.
It might be interesting to note that the CSS3 specification defines 147 or so color keywords that you can use in your style sheets. However, if you do, your CSS code will not be able to validate as an older specification style sheet because the older specifications do not include those keyword values. So Instead, rewrite or update the entire CSS code to CSS3 specifications or use a different method to define your colors, such as an RGB triplets or Hex.
Here are several features new to CSS3:
With the CSS3 border-radius property, you can give any element
"rounded corners".
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.
Numbers followed by -webkit- or -moz- specify the first version that worked with a prefix.
| Property |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| border-radius | 9.0 | 5.0 4.0 -webkit- |
4.0 3.0 -moz- |
5.0 3.1 -webkit- |
10.5 |
With CSS3, you can give any element "rounded corners", by using the
border-radius property.
Here are three examples:
1. Rounded corners for an element with a specified background color:
Rounded corners!
2. Rounded corners for an element with a border:
Rounded corners!
3. Rounded corners for an element with a background image:
Rounded corners!
NOTE: All of the following examples are either division or global elements intended to be used in style sheets or in style blocks. Be sure to use the proper element blocks and HTML in order for the example to display properly in the "Try-It Editor"
Here is the code:
 |
Tip: the border-radius property is actually a
shorthand property for the border-top-left-radius,
border-top-right-radius,
border-bottom-right-radius and
border-bottom-left-radius properties. |
|---|
If you specify only one value for the border-radius property,
this radius will be applied to all 4 corners.
However, you can specify each corner separately if you wish. Here are the rules:
Here are three examples:
1. Four values - border-radius: 15px 50px 30px 5px:
2. three values - border-radius: 15px 50px 30px:
3. Two values - border-radius: 15px 50px:
Here is the code:
You could also create elliptical corners:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| border-radius | A shorthand property for setting all the four border-*-*-radius properties |
| border-top-left-radius | Defines the shape of the border of the top-left corner |
| border-top-right-radius | Defines the shape of the border of the top-right corner |
| border-bottom-right-radius | Defines the shape of the border of the bottom-right corner |
| border-bottom-left-radius | Defines the shape of the border of the bottom-left corner |
With the CSS3 border-image property, you can set an image to be
used as the border around an
element.
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.
Numbers followed by -webkit-, -moz-, or -o- specify the first version that worked with a prefix.
| Property |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| border-image | 11.0 | 16.0 4.0 -webkit- |
15.0 3.5 -moz- |
6.0 3.1 -webkit- |
15.0 11.0 -o- |
The CSS3 border-image property allows you to specify an image to
be used instead of the normal border around an element.
The property has three parts:
We will use the following image (called "border.png"):
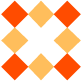
The border-image property takes the image and slices it into
nine sections, like a tic-tac-toe board. It then places the corners at the
corners, and the middle sections are repeated or stretched as you
specify.
Note: For border-image to work, the element
also needs the border property set!
Here, the middle sections of the image are repeated to create the border:
An image as a border!
Here is the code:
Here, the middle sections of the image are stretched to create the border:
An image as a border!
Here is the code:
 |
Tip: the border-image property is actually a
shorthand property for the border-image-source,
border-image-slice, border-image-width,
border-image-outset and border-image-repeat
properties. |
|---|
Different slice values completely changes the look of the border:
Example 1:
border-image: url(images/border.png) 50% round;
Example 2:
border-image: url(images/border.png) 20% round;
Example 3:
border-image: url(images/border.png) 30% round;
Here is the code:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| border-image | A shorthand property for setting all the border-image-* properties |
| border-image-source | Specifies the path to the image to be used as a border |
| border-image-slice | Specifies how to slice the border image |
| border-image-width | Specifies the widths of the border image |
| border-image-outset | Specifies the amount by which the border image area extends beyond the border box |
| border-image-repeat | Specifies whether the border image should be repeated, rounded or stretched |
CSS3 contains a few new background properties, which allow greater control of the background element.
In this chapter you will learn how to add multiple background images to one element.
You will also learn about the following new CSS3 properties:
background-sizebackground-originbackground-clipThe numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.
Numbers followed by -webkit-, -moz-, or -o- specify the first version that worked with a prefix.
| Property |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| background-image (with multiple backgrounds) |
9.0 | 4.0 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 11.5 |
| background-size | 9.0 | 4.0 1.0 -webkit- |
4.0 3.6 -moz- |
4.1 3.0 -webkit- |
10.5 10.0 -o- |
| background-origin | 9.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 10.5 |
| background-clip | 9.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 10.5 |
CSS3 allows you to add multiple background images for an element, through the
background-image property.
The different background images are separated by commas, and the images are stacked on top of each other, where the first image is closest to the viewer.
The following example has two background images, the first image is a flower (aligned to the bottom and right) and the second image is a paper background (aligned to the top-left corner):
Multiple background images can be specified using either the individual
background properties (as above) or the background shorthand
property.
The following example uses the background shorthand property
(same result as example above):
The CSS3 background-size property allows you to specify the size
of background images.
Before CSS3, the size of a background image was the actual size of the image. CSS3 allows us to re-use background images in different contexts.
The size can be specified in lengths, percentages, or by using one of the two keywords: contain or cover.
The following example resizes a background image to much smaller than the original image (using pixels):
Original background image:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat.
Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Resized background image:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diam nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut laoreet dolore magna aliquam erat volutpat.
Ut wisi enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tation ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Here is the code:
The two other possible values for background-size are
contain and
cover.
The contain keyword scales the background image to be as large
as possible (but both its width and its height must fit inside the content
area). As such, depending on the proportions of the background image and the
background positioning area, there may be some areas of the background which
are not covered by the background image.
The cover keyword scales the background image so that the
content area is completely covered by the background image (both its width and
height are equal to or exceed the content area). As such, some parts of the
background image may not be visible in the background positioning area.
The following example illustrates the use of contain and
cover:
The background-size property also accepts multiple values for
background size (using a comma-separated list), when working with multiple
backgrounds.
The following example has three background images specified, with different background-size value for each image:
Now we want to have a background image on a website that covers the entire browser window at all times.
The requirements are as follows:
The following example shows how to do it; Use the html element (the html element is always at least the height of the browser window). Then set a fixed and centered background on it. Then adjust its size with the background-size property:
The CSS3 background-origin property specifies where the
background image is positioned.
The property takes three different values:
The following example illustrates the background-origin
property:
The CSS3 background-clip property specifies the painting area of
the background.
The property takes three different values:
The following example illustrates the background-clip
property:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| background | A shorthand property for setting all the background properties in one declaration |
| background-clip | Specifies the painting area of the background |
| background-image | Specifies one or more background images for an element |
| background-origin | Specifies where the background image(s) is/are positioned |
| background-size | Specifies the size of the background image(s) |
CSS supports color names, hexadecimal and RGB colors.
In addition, CSS3 also introduces:
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports CSS3 color values/property.
| Property |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGBA, HSL, and HSLA | 9.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 10.1 |
| opacity | 9.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 10.1 |
RGBA color values are an extension of RGB color values with an alpha channel which specifies the opacity for a color.
An RGBA color value is specified with: rgba(red, green, blue, alpha). The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (fully opaque).
The following example defines different RGBA colors:
HSL stands for Hue, Saturation and lightness.
An HSL color value is specified with: hsl(hue, saturation, lightness).
The following example defines different HSL colors:
HSLA color values are an extension of HSL color values with an alpha channel which specifies the opacity for a color.
An HSLA color value is specified with: hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, alpha), where the alpha parameter defines the opacity. The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (fully opaque).
The following example defines different HSLA colors:
The CSS3 opacity property sets the opacity for a specified RGB value.
The opacity property value must be a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (fully opaque).
Notice that the text above will also be opaque.
The following example shows different RGB values with opacity:
There are 140 color names predefined in the HTML and CSS color specification. Refer to this table of predefined color names.